通常のdelaunay三角形網では、局所最小角最大化の方針に従って三角形網を作成していきますが、
そこに制約として、必ず三角形の1辺となるように線分を追加することが良くあります。

通常ならこう分割される

赤い制約線を入れることで、分割を制御する
これを制約付きdelaunay分割(CDT)と呼びます。
gtsライブラリでもCDTを作成することができます。
付属サンプルのdelaunay.cをみると、通常のdelaunay三角形網を作成し終わった後で、
制約線をsurfaceに追加しているようです。
以下の例は、shapelibを使って点群Shapeファイルと制約線Shapeファイルを読み込み、
CDT網を作成する例です。
この例では制約線のZ値を10、点群のZ値を0として扱っています。
1: 2: #include "gts.h" 3: #include "shapefil.h" 4: #include <stdlib.h> 5: 6: static void add_constraint( GtsConstraint *c, GtsSurface *s ) 7: { 8: g_assert( gts_delaunay_add_constraint(s, c) == NULL ); 9: } 10: 11: int main( int argc, char *argv[] ) 12: { 13: GPtrArray *vertices; 14: GtsFifo * edges; 15: GSList *list = NULL; 16: GtsTriangle *t; 17: GtsSurface *surface; 18: GtsVertex *v1, *v2, *v3; 19: SHPHandle hShp; 20: SHPObject *psElem; 21: int nShapeType, nEntities, iPartStart = 0, iPartEnd; 22: double adfMinBound[4], adfMaxBound[4]; 23: guint i, j, k, x = 0; 24: 25: hShp = SHPOpen( argv[1], "r" ); 26: if ( hShp == NULL ) 27: { 28: exit( 1 ); 29: } 30: 31: SHPGetInfo( hShp, &nEntities, &nShapeType, adfMinBound, adfMaxBound ); 32: if ( nShapeType != SHPT_POINT && 33: nShapeType != SHPT_POINTZ && 34: nShapeType != SHPT_POINTM ) 35: { 36: SHPClose( hShp ); 37: exit( 1 ); 38: } 39: 40: // 頂点配列の作成 41: vertices = g_ptr_array_new(); 42: 43: // ファイルからデータを読み込んで頂点配列に追加 44: for ( i = 0; i < (guint)nEntities; i++ ) 45: { 46: psElem = SHPReadObject( hShp, i ); 47: 48: for ( j = 0; j < (guint)psElem->nVertices; j++ ) 49: { 50: g_ptr_array_add( vertices, 51: gts_vertex_new( gts_vertex_class(), 52: psElem->padfX[0], psElem->padfY[0], psElem->padfZ[0] ) ); 53: x++; 54: } 55: 56: SHPDestroyObject( psElem ); 57: } 58: 59: SHPClose( hShp ); 60: 61: // 制約線Shape読み込み 62: hShp = SHPOpen( argv[2], "r" ); 63: if ( hShp == NULL ) 64: { 65: exit( 1 ); 66: } 67: 68: edges = gts_fifo_new (); 69: 70: SHPGetInfo( hShp, &nEntities, &nShapeType, adfMinBound, adfMaxBound ); 71: if ( nShapeType != SHPT_ARC && 72: nShapeType != SHPT_ARCZ && 73: nShapeType != SHPT_ARCM ) 74: { 75: SHPClose( hShp ); 76: g_ptr_array_free( vertices, TRUE ); 77: exit( 1 ); 78: } 79: 80: for ( i = 0; i < (guint)nEntities; i++ ) 81: { 82: psElem = SHPReadObject( hShp, i ); 83: 84: for ( j = 0; j < (guint)psElem->nParts; j++ ) 85: { 86: iPartEnd = j != psElem->nParts - 1 ? 87: psElem->panPartStart[j+1] - 1 : 88: psElem->nVertices; 89: 90: g_ptr_array_add( vertices, 91: gts_vertex_new( gts_vertex_class(), 92: psElem->padfX[0], psElem->padfY[0], 10.0 ) ); 93: x++; 94: for ( k = iPartStart+1; k < (guint)iPartEnd; k++ ) 95: { 96: g_ptr_array_add( vertices, 97: gts_vertex_new( gts_vertex_class(), 98: psElem->padfX[k], psElem->padfY[k], 10.0 ) ); 99: x++; 100: 101: gts_fifo_push( edges, 102: gts_edge_new( GTS_EDGE_CLASS(gts_constraint_class()), 103: (GtsVertex *)g_ptr_array_index(vertices, x-2), 104: (GtsVertex *)g_ptr_array_index(vertices, x-1) ) ); 105: } 106: } 107: } 108: 109: SHPClose( hShp ); 110: 111: // 頂点配列をリストにコピー 112: for ( i = 0; i < vertices->len; i++ ) 113: list = g_slist_prepend( list, g_ptr_array_index( vertices, i ) ); 114: 115: // 全頂点を確実に包含する三角形を作成 116: t = gts_triangle_enclosing( gts_triangle_class(), list, 100. ); 117: g_slist_free( list ); 118: gts_triangle_vertices( t, &v1, &v2, &v3 ); 119: 120: // 包含三角形からGtsSurfaceを作成 121: surface = gts_surface_new( gts_surface_class(), 122: gts_face_class(), 123: gts_edge_class(), 124: gts_vertex_class() ); 125: 126: gts_surface_add_face( surface, gts_face_new( gts_face_class(), 127: t->e1, t->e2, t->e3) ); 128: 129: // 包含三角形にファイルの頂点を1つずつ追加 130: // 追加された頂点と包含三角形は常にdelaunay分割になっている 131: for ( i = 0; i < vertices->len; i++ ) 132: { 133: GtsVertex * vi = (GtsVertex *)g_ptr_array_index (vertices, i); 134: GtsVertex * v = gts_delaunay_add_vertex (surface, vi, NULL); 135: 136: g_assert (v != vi); 137: if (v != NULL) 138: { 139: gts_vertex_replace (vi, v); 140: } 141: } 142: 143: // 読み込んだ頂点配列を開放 144: g_ptr_array_free( vertices, TRUE ); 145: 146: // 制約線の追加 147: gts_fifo_foreach( edges, (GtsFunc)add_constraint, surface ); 148: 149: // 制約線キューの削除 150: gts_fifo_destroy( edges ); 151: 152: // 包含三角形の頂点だけを削除 153: gts_allow_floating_vertices = TRUE; 154: gts_object_destroy (GTS_OBJECT (v1)); 155: gts_object_destroy (GTS_OBJECT (v2)); 156: gts_object_destroy (GTS_OBJECT (v3)); 157: gts_allow_floating_vertices = FALSE; 158: 159: // 三角形網を書き出し 160: gts_surface_write (surface, "test.gts"); 161: 162: gts_object_destroy( GTS_OBJECT( surface ) ); 163: 164: return 0; 165: }
注意点は大体以下のとおりです。
制約線の登録
制約線は線分として登録します。
したがって、連続線分はそれぞれ線分に分解して1つずつ登録する必要があります。
また、制約線の頂点はdelaunay三角形網を作成する際の頂点群に使用する点データに
含まれているデータである必要があります。
そのため、制約線の登録部分(101〜104行目)はあんなややこしい指定の仕方になっています。
制約線の適用
この例では制約線をキューに溜め込んで、gts_fifo_foreach()関数で適用しています。
この方式の場合は適用関数のポインタを渡す必要があるので、
それ用の関数add_constraint()をわざわざ作っています。
直接gts_delaunay_add_constraint()を使用してもたぶん大丈夫です。
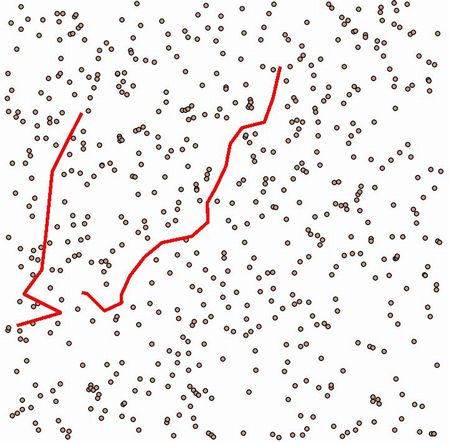
入力データ
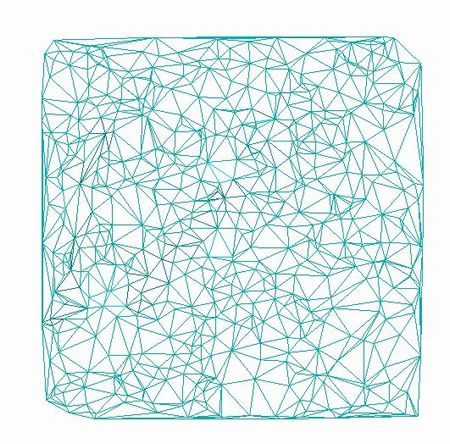
出力結果

